Why Do Plants Need Nitrogen?
Nitrogen performs some of the most important tasks within a plant:
- Component of chlorophyll (which plants need in order to photosynthesize their own food from sunlight)
- Synthesizes amino acids, proteins, and enzymes that help the plant form news cells and tissues as it grows
The Nitrogen Cycle
Earth’s atmosphere contains about 78% nitrogen (N2). Plants cannot use nitrogen in its N2 form, so it must be transformed through a process called the nitrogen cycle. Throughout the nitrogen cycle, N2 changes into different compounds: (nitrogen oxides, ammonium, and nitrates) and becomes available for plants to use. Let’s take a closer look at the different stages of the nitrogen cycle.
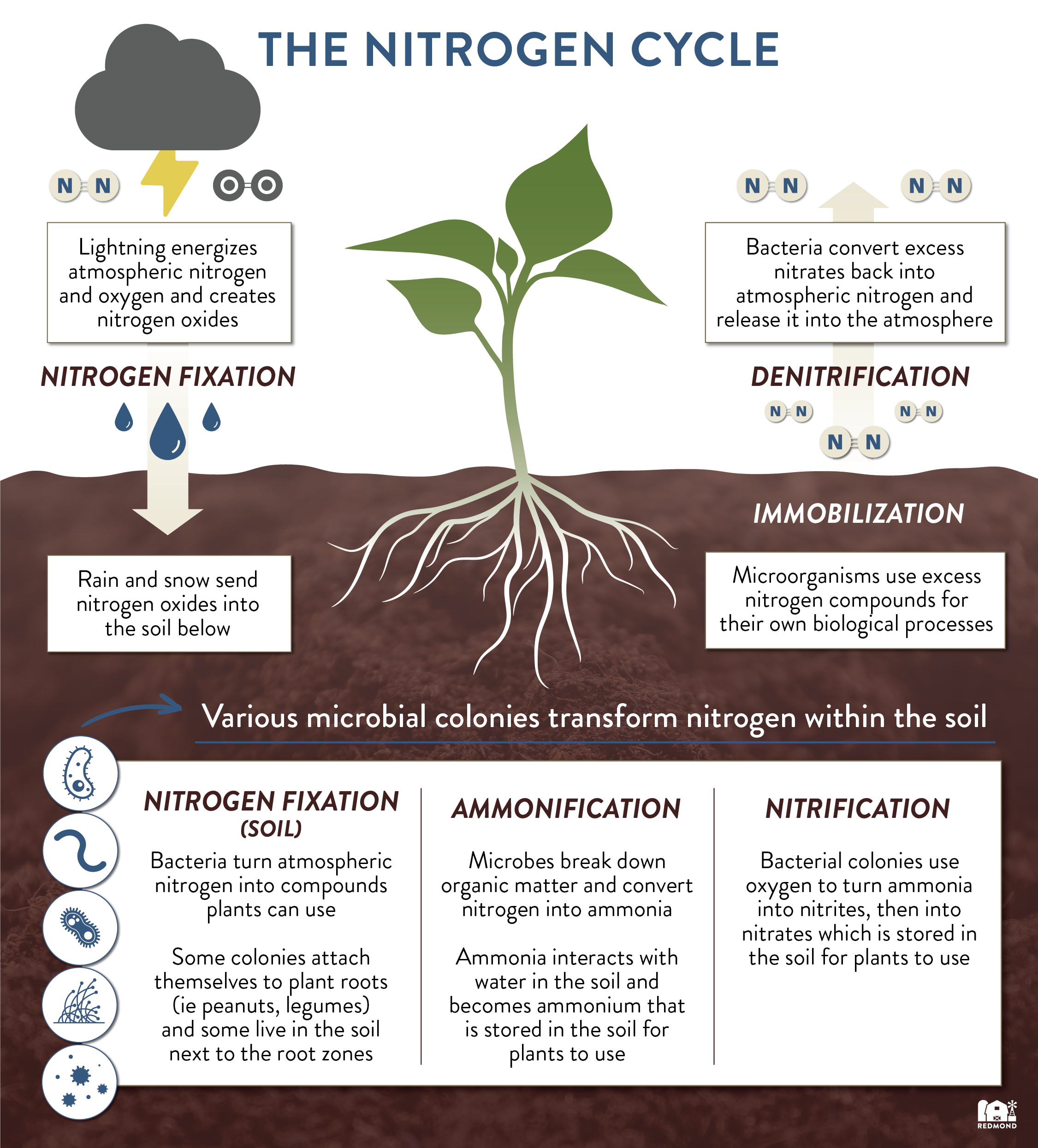
1. Nitrogen Fixation
There are a number of natural and industrial processes that can change or “fix” atmospheric nitrogen into usable compounds.
Lightning/Precipitation
Lightning strikes release spurts of energy and cause atmospheric nitrogen to react with atmospheric oxygen and create nitrogen oxides. Rain and snow then deposit these nitrogen compounds into the soil.
Industrial Fertilizer
Using heat and pressure, fertilizer manufacturers can combine nitrogen and hydrogen to make ammonia. Ammonia is then further processed to create ammonium nitrate fertilizer which can be mixed into the soil for plants to use.
Bacterial Fixation
Most nitrogen fixation occurs directly in the soil itself, thanks to helpful colonies of bacteria. For some plants (like peanuts and legumes), these colonies attach directly to the roots and fix nitrogen into usable forms for the plant. For other plants, these colonies live in the soil surrounding the roots instead of direct attachments. The resulting fixed nitrogen compounds are not just beneficial to the plant, but to all other organisms living in the soil.
2. Ammonification
Microbes in the soil break down organic matter (like decomposing plant and animal matter) and convert nitrogen into ammonia . Ammonia then interacts with water in the soil and becomes ammonium. This ammonium is stored in the soil for plants to use.
3. Nitrification
Bacterial colonies use oxygen to turn ammonia first into nitrites, then into nitrates thus creating another nitrogen compound plants can use in the soil.
4. Immobilization
Micro-organisms in the soil need nitrogen in order to survive just like plants do. These organisms use ammonium and nitrates from the soil for their own biological processes. Immobilization is an important process that helps balance out excess nitrogen in the soil.
5. Denitrification
Denitrifying bacteria, in the soil, convert excess nitrates back into atmospheric nitrogen and release it back into the atmosphere.
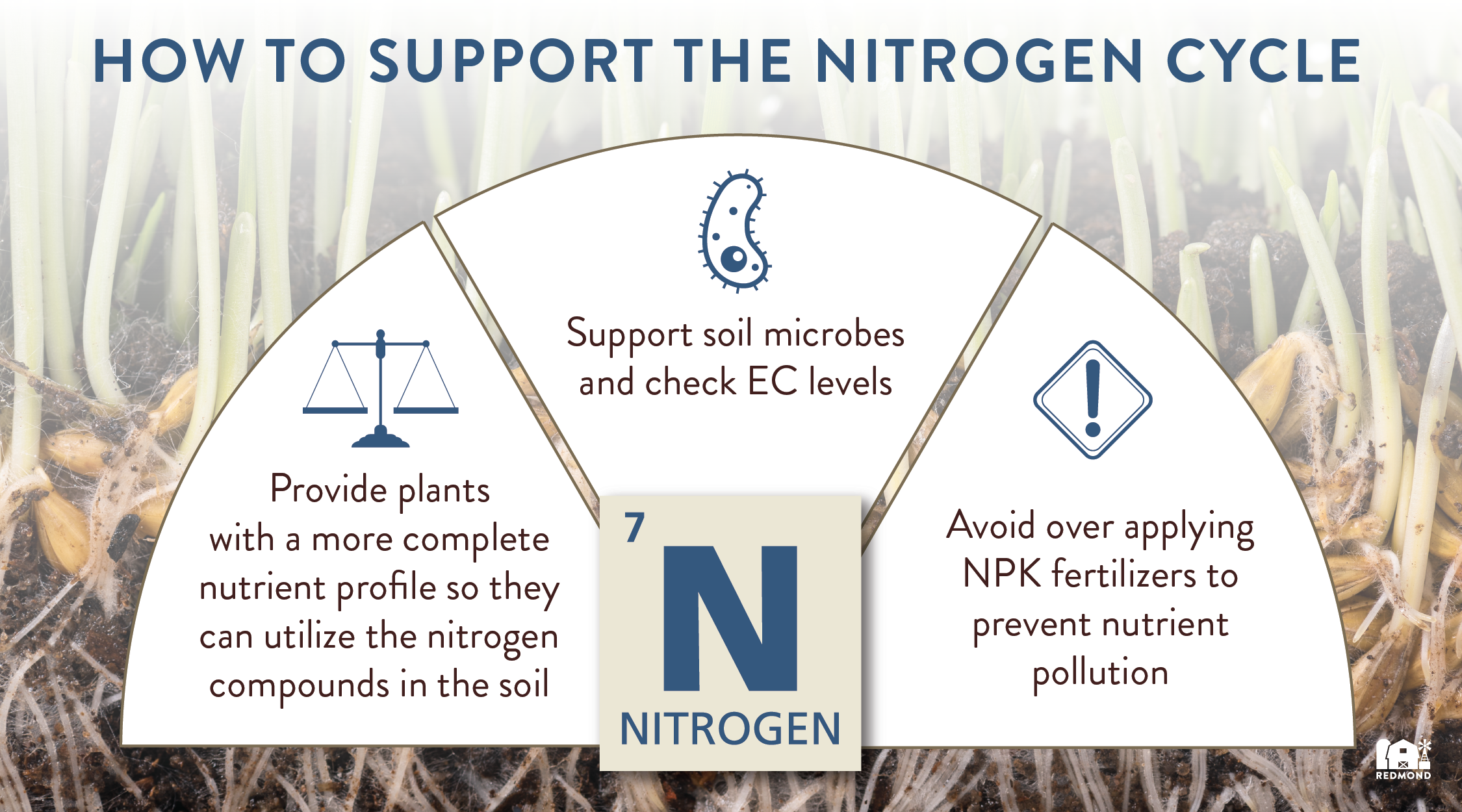
Don’t Just Rely On Nitrogen Fertilizers
As important as nitrogen is, it is only part of the plant health puzzle. Some plant nutrient programs focus too heavily on nitrogen and neglect the rest of the picture. Here are a few best practices to help your plants get the most out of their nitrogen.
A recent series of studies conducted by the University of Illinois, found that plants prefer naturally occurring nitrogen over chemical nitrogen fertilizers. Traceable biomarkers were used to distinguish between applied nitrogen fertilizers and soil-based (bacteria created) nitrogen.
- These 4 studies found that corn crops only took in 21% of the nitrogen fertilizer...the rest remained wasted in the soil.
- 67% of the crops' nitrogen intake was from soil-based, bacteria formed nitrogen, not chemical fertilizer.
Trace Mineral Supplements
Plants need a balanced nutrient profile of macro-minerals and micro-minerals. Some of these minerals also help plants process and utilize nitrogen. If these trace minerals are missing from your soil, your plants can show signs of nitrogen deficiency even if nitrogen compounds are actually present in the soil.
- Manganese: helps plant synthesize chlorophyll and absorb nitrogen
- Magnesium: joins with nitrogen to form the chlorophyll molecule
- Molybdenum: forms enzymes needed for nitrogen fixation
Traditional nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers (NPK) often neglect these trace minerals, so make sure you are providing your plants with a broad and balanced nutrient profile.
Microbe Activity/Electrical Conductivity
The nitrogen cycle relies upon healthy colonies of microorganisms in the soil. If the electrical conductivity (EC) of your soil is low, microbes will not be active enough to make nitrogen available to your plants.
• Learn more about improving the EC levels in your soil.
Nitrogen Pollution
Immobilizing and denitrifying bacteria do their best to take care of excess nitrogen compounds in the soil...but they can only do so much. Over applying nitrogen based fertilizers can cause eutrophication or “nutrient pollution.” As rain falls, water leaches all that excess nitrogen into waterways and it is devastating to aquatic health. Excess nitrogen creates:
- High biochemical oxygen demand: When high levels of nitrogen enter our waterways, the microorganisms feast on the excess nutrients and deplete the water of dissolved oxygen.
- Aquatic dead zones: The plummeting levels of dissolved oxygen can kill off large quantities of aquatic life in collection basins and estuaries.
- Harmful algae blooms: Excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers also causes toxic algae blooms in our waterways.
*The moral of the story…
- Be careful in your application of NPK fertilizers to your crops
- Look beyond just NPK and provide a balanced nutrient profile so your crops can have the tools they need to use nitrogen compounds in the soil
- Monitor your soil’s EC levels to make sure your soil microbes are actively involved in the nitrogen cycle
Mineral Supplements From Redmond Minerals
Redmond Minerals has enjoyed sharing our rich, Jurassic Era mineral deposit to support healthy farming for over 50 years. Our goal to nourish the world from the ground up starts with replenishing our soils. Redmond’s soil amendments have helped growing operations across the country replenish soil health, grow more nutrient dense crops, and increase yields.

- With a full spectrum of sea minerals, our soil amendments can improve EC levels to stimulate microbe activity in your soil
- These trace minerals also provide your plants with the building blocks they need to utilize nitrogen
Give us a call at  today to learn how our soil program can help you grow more delicious, productive, and nutrient dense crops.
today to learn how our soil program can help you grow more delicious, productive, and nutrient dense crops.
© 2023 Redmond Minerals Inc.

